-
Nest.js 개요와 라이프 사이클카테고리 없음 2022. 2. 9. 17:33
Nest.js 개요
- Nest.js는 Node.js의 프레임 워크이다. 확장이 쉬우며, rest-api, graphql, microservice(non-http), websocket 의 템플릿을 cli 를 통해 자동으로 생성 해준다.
- Express/Fastify 기반의 서버를 제공한다.
- IoC를 구현 하는 프레임 워크로, 객체를 관리하고 생성을 책임지고 의존성을 관리하는 컨테이너이다.
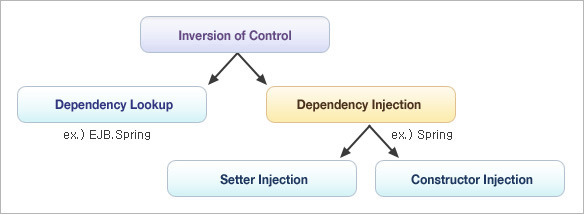
- IoC란 제어의 역전 이란 말인데, 메서드나 객체의 호출작업을 개발자가 결정하는 것이 아니라 제어권을 제 3자(컨테이너) 에게 위임하는 것이다.
- DI와 밀접하게 관련이 되어있는데 아래 사진을 참고하면 될듯 하다.
Nest.js 라이프 사이클
기본적인 순서는 다음과 같다.
Middleware => Guards => Pre-Interceptors => Pipes => Controller => Service => Post-Interceptors => ExceptionFilter => Response
1. Middleware
전역으로 바인딩 되어있는 미들웨어를 가장먼저 실행 한다. (main.ts 에 app.use로 바인딩 되어있는 미들웨어들)
Express와 비슷한 방식으로 바인딩 된 순서대로 순차적으로 실행 된다.
app.use(cookieParser(process.env.SESSION_SECRET)); app.use(helmet()); app.use(helmet.xssFilter()); app.use(helmet.noSniff()); app.use(helmet.hidePoweredBy()); app.use(helmet.referrerPolicy()); app.use(bodyParser.json());2. Guards
사용자의 권한을 체크하는 로직이 들어간다 예를들어 jwt를 사용한다면 @UseGuards()를 통해 jwt의 값이 유효한지 검사 할 수 있다.
import { Injectable, CanActivate, ExecutionContext } from '@nestjs/common'; import { Observable } from 'rxjs'; @Injectable() export class AuthGuard implements CanActivate { canActivate( context: ExecutionContext, ): boolean | Promise<boolean> | Observable<boolean> { const request = context.switchToHttp().getRequest(); return validateRequest(request); } }다음과 같이 Guards를 정의 해놓으면 컨트롤러에선 이렇게 사용 할 수 있다.
@Controller('cats') @UseGuards(RolesGuard) export class CatsController {}3. Interceptor
인터셉터는 컨트롤러에 접근하기 전, 후에서 바인딩 시킬 수 있다.
컨트롤러에 전에 접근하기 전에 사용하려면 return 전에 사용을하면 되고 컨트롤러 접근후에 사용하려면 return 문에서 사용하면 된다.
import { Injectable, NestInterceptor, ExecutionContext, CallHandler } from '@nestjs/common'; import { Observable } from 'rxjs'; import { tap } from 'rxjs/operators'; @Injectable() export class LoggingInterceptor implements NestInterceptor { intercept(context: ExecutionContext, next: CallHandler): Observable<any> { console.log('Before...'); const now = Date.now(); return next .handle() .pipe( tap(() => console.log(`After... ${Date.now() - now}ms`)), ); } }그리고 컨트롤러에 Guard와 동일하게 걸어놓으면 된다.
@UseInterceptors(LoggingInterceptor) export class CatsController {}4. Pipes
요청이 들어오는 파라미터의 validation 혹은 형변환이 필요할 때 파이프에서 진행 한다.
@Get(':id') async findOne(@Param('id', ParseIntPipe) id: number) { return this.catsService.findOne(id); }5. Controller
routing ,http method, Request에 담긴 페이로드, Response에 담을 페이로드를 Controller에서 관리할 수 있다.
import { Controller, Get, Req } from '@nestjs/common'; import { Request, Response } from 'express'; @Controller('cats') export class CatsController { @Get() findAll(@Req() request: Request, /*@Res() response: Response*/): string { return 'This action returns all cats'; } }6. Service
실제 비지니스 로직을 Service 단 에서 관리 할 수 있다.
import { Injectable } from '@nestjs/common'; import { Cat } from './interfaces/cat.interface'; @Injectable() export class CatsService { private readonly cats: Cat[] = []; create(cat: Cat) { this.cats.push(cat); } findAll(): Cat[] { return this.cats; } }7. ExceptionFilter
익셉션 필터는 로직을 처리하다가 오류가 발생 하면 HttpException을 throw 하게 된다.
@Get() async findAll() { throw new HttpException('Forbidden', HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN); }